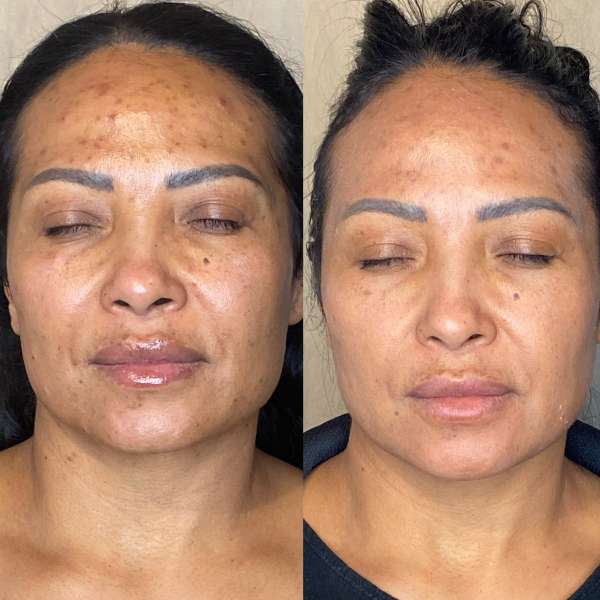
What is a Chemical Peel?
A chemical peel is a cosmetic procedure that uses a chemical solution to exfoliate the skin, removing damaged outer layers and revealing smoother, fresher skin underneath. The intensity and recovery time vary depending on the type and depth of the peel.
Types of Chemical Peels
Chemical peels are categorized by their depth of penetration, which determines the concentration and type of acid used.
Light (Superficial) Peels
- Active ingredients: Mild acids like glycolic, lactic, or salicylic acid.
- Purpose: Exfoliates only the outer layer of the skin (epidermis).
- Treats fine lines, mild acne, and uneven skin tone.
- Recovery: Minimal downtime, with mild redness and flaking lasting a few days.
Medium Peels
- Active ingredients: Trichloroacetic acid (TCA).
- Purpose: Removes skin cells from the epidermis and the upper part of the middle skin layer (dermis).
- Used to treat wrinkles, acne scars, and more pronounced skin discoloration.
- Recovery: Requires a recovery time of 7 to 14 days, with redness and swelling that can last for months.
Deep Peels
- Active ingredients: Carbolic acid (phenol).
- Purpose: The most intensive peel, reaching the lower layer of the dermis.
- Used for deep wrinkles, severe sun damage, and significant scarring.
- Recovery: Significant downtime, with severe redness and swelling that can take weeks to heal and months to resolve completely.
Benefits of a Chemical Peel
- Reduces signs of aging: Minimizes the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by promoting new collagen production.
- Improves skin texture: Exfoliates dead skin cells to create a smoother, softer skin surface.
- Treats acne: Unclogs pores and minimizes breakouts, with salicylic acid peels being particularly effective for oily and acne-prone skin.
- Evens skin tone: Reduces the appearance of dark spots, sun damage, and hyperpigmentation.
- Minimizes pores: Helps refine and diminish the appearance of large pores.
Risks and Side Effects
- Redness, swelling, and scabbing: Common, especially with medium and deep peels.
- Changes in skin color: Treated skin may temporarily or permanently become darker (hyperpigmentation) or lighter (hypopigmentation).
- Scarring: A rare but possible side effect, usually from improper aftercare.
- Infection: Can trigger bacterial, fungal, or viral infections, such as a herpes simplex flare-up.
- Organ damage: The chemical phenol used in deep peels can be toxic to the heart, kidneys, and liver.
Aftercare and Recovery
- Cleanse gently: Use a mild, non-foaming cleanser with lukewarm water.
- Avoid picking: Let peeling skin or scabs fall off naturally to prevent scarring and infection.
- Keep skin hydrated: Use a recommended moisturizer, but don’t over-moisturize.
- Practice sun protection: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30+) daily, wear a hat, and avoid direct sun exposure.
- Avoid harsh products: Steer clear of retinoids, other exfoliants, and alcohol-based toners until your skin is fully healed.
How it Works
Application
Controlled exfoliation
Peeling
Skin regeneration
have a question?
Quick answers to questions you may have
Is a chemical peel right for me?
A: Consult a qualified professional like a dermatologist to discuss your medical history, skin concerns, and expectations.
How long does it take to recover from a chemical peel?
Recovery time varies depending on the type and depth of the peel, ranging from a few days to several weeks.
Can I get a chemical peel if I'm pregnant or breastfeeding?
It’s best to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare provider before undergoing a chemical peel during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
How long do the results of a chemical peel last?
The results can last for several months to a year or more, depending on the type of peel and individual skin concerns.